Benefits professionals and HR leaders face the enormous challenge of designing effective employee benefits packages that serve up to four distinct generations working side by side. The complexity of this task continues to grow, with SHRM's latest data revealing a 23% increase in available benefits options in just the past two years – from 175 in 2023 to 216 in 2024.
This expansion reflects more than just market innovation; it underscores the critical need for employers and plan administrators to understand what drives the benefits preferences of each generation. Two-thirds (66%) of employees believe benefits hold equal or more importance than salary, and 75% say they're more likely to stay with their organization due to the benefits package. Despite the increased demand for competitive benefits, less than half (43%) of employees report being satisfied with their current benefits package, underscoring the urgent need to re-evaluate traditional approaches.
During and since the 2020-21 pandemic, work, benefits, and work-life integration have undergone fundamental transformations across all generations, creating both new common ground and emerging divides. In this evolving environment, benefits professionals must take a strategic approach that balances universal needs with generation-specific preferences.
This whitepaper offers insights and practical solutions for navigating the challenges of multi-generational workplaces and delivering effective benefits strategies to employer groups.
The Multigenerational Workforce Landscape
The modern workplace spans nearly six decades of birth years, creating a unique dynamic where employees with vastly different formative experiences must collaborate daily.
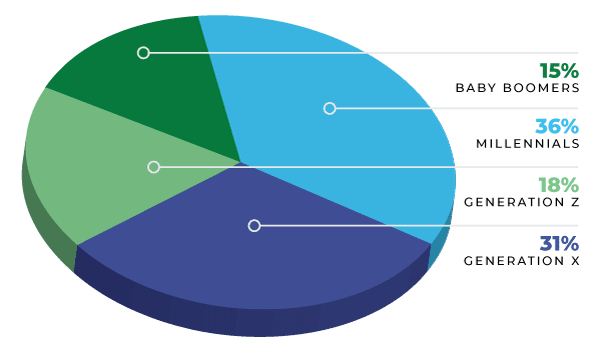
According to recent U.S. Department of Labor data, Millennials and Gen Z now make up more than half of the workforce.
Millennials comprise more than one-third of the U.S. workforce, Gen X represents another third, while Gen Z makes up nearly one-fifth, and Boomers account for about 15%. Each generation brings distinct perspectives shaped by historical events, technological evolution, and economic circumstances.
Gen Z (1997-2012): Realistic Innovators
Generation Z workers, now entering the workforce in significant numbers, bring perspectives shaped by global connectivity, social media saturation, and economic uncertainty. This generation tends to prioritize mental health support and flexible work arrangements more than their predecessors, while maintaining a pragmatic approach to career security.
As digital natives with entrepreneurial mindsets, Gen Z workers prioritize personal brand building while maintaining realistic expectations about finances and career progression. They value diversity, inclusion, and social responsibility, expecting employers to demonstrate these values through concrete actions and benefits.
Millennials (1981-1996): Purpose-Driven Optimizers
Now in their late 20s to early 40s, Millennials represent the largest segment of today's workforce. Economic turbulence during their formative career years, like the 2008 financial crisis and the pandemic, shaped their perspective on work, money, and career stability.
Millennials bring a purpose-driven, values-oriented approach to work, with high expectations for digital integration and meaningful employment. They prioritize work-life integration over traditional work-life balance, seeking professional development opportunities and social impact, alongside competitive compensation and benefits.
Generation X (1965-1980): Pragmatic Balancers
Currently in their 40s and 50s, Generation X finds itself in the challenging "sandwich generation" position – simultaneously caring for aging parents while supporting their own children. Having lived through significant economic upheaval, including multiple recessions and widespread corporate downsizing, they approach work-life balance with hard-earned pragmatism and healthy skepticism of corporate promises.
This generation values independence and self-reliance, balancing career ambitions with family responsibilities. They prioritize practical benefits, such as flexible spending accounts and dependent care assistance, alongside professional development opportunities that support career advancement without compromising family obligations.
Baby Boomers (1946-1964): Security Seekers
Now primarily in their 60s and 70s, Baby Boomers represent the most experienced segment of the workforce. While many Boomers plan to or have entered retirement, a growing trend of returning to work after initial retirement continues to impact workplace demographics. This generation's career-focused mindset emphasizes loyalty, hierarchy, and traditional work structures.
Boomers demonstrate a strong work ethic and dedication to career advancement, preferring face-to-face communication and traditional management approaches. Their benefits priorities center on comprehensive health insurance, robust retirement planning, and increasingly, long-term care options. Job security and established benefit structures remain top concerns.
The Pandemic and Its Lasting Impact on Expectations
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a generational equalizer, by accelerating existing trends (such as digital adoption) and creating new shared priorities across age groups (like mental health awareness and financial wellness). However, the subsequent economic recovery has also introduced new challenges that affect generations differently, fundamentally reshaping employees' benefits expectations.

Accelerated
Digital Adoption
The forced, rapid digital transformation bridged generational technology gaps, with older generations quickly adapting to remote work technologies.
This shift created more common ground between generations regarding digital tools and flexible work arrangements, fundamentally changing expectations for how benefits are delivered and accessed.

Universal Mental
Health Awareness
Perhaps most significantly, the pandemic elevated mental health from a generational preference to a universal priority. Recent research shows that 77% of large employers report an increase in mental health needs among their workforce, with 47% of employees citing work stress as the primary cause of deteriorating mental health.
Organizations now recognize that mental health support is essential for productivity and retention across all demographics, with mental health and well-being becoming the most popular employee benefit category in 2025.

Healthcare as a
Non-Negotiable
The pandemic reinforced comprehensive healthcare coverage as a collective necessity, with all generations now viewing robust health benefits as non-negotiable.
Telehealth services, once met with resistance from older generations, gained widespread acceptance during the crisis and remain a valued benefit across all age groups.
Financial Wellness: The Universal Benefits Need
Financial wellness has emerged as a leading cross-generational benefits trend, with specific applications varying by life stage and generational priorities.
Economic uncertainty created financial stress across generations, driving increased demand for financial wellness programs, emergency savings assistance, and flexible benefit options. This shift transformed financial wellness from a nice-to-have perk into a strategic necessity.
Healthcare Cost Escalation
Healthcare costs continue to outpace general inflation, affecting all generations differently. Older generations tend to have higher utilization rates, while younger generations may prioritize preventive care and mental health services. Smart benefits design addresses these varying needs through tiered coverage options and wellness incentives.
The Student Debt Crisis
Mounting student debt crisis particularly affects Millennials and Generation Z, making student loan assistance programs a powerful recruitment and retention tool. With total student debt exceeding $1.7 trillion nationally, employers who offer meaningful student loan assistance gain a significant competitive advantage.
Emergency Savings: A Pandemic-Driven Priority
The pandemic underscored the crucial importance of emergency savings across all generations. Organizations can help employees build financial resilience through emergency savings programs, financial hardship assistance, and flexible benefit options.
Housing Market Pressures
The challenging housing market disproportionately affects Millennials and Generation Z, giving employers a chance to stand out through homeownership assistance, housing stipends, or relocation support programs.
Retirement Planning Across Generations
Retirement planning needs vary across generations:
- Baby Boomers need to focus on optimizing their retirement income and planning for healthcare costs. Key strategies include maximizing Social Security benefits and making informed Medicare decisions.
- Generation X benefits from emphasis on catch-up contributions and retirement readiness assessments, helping them maximize their remaining earning years while balancing current family obligations.
- Millennials require foundational retirement education, combined with debt management strategies, to help them balance immediate financial pressures with long-term planning needs.
- Generation Z responds well to basic financial literacy programs and the introduction of long-term planning, establishing good habits early in their careers.
Benefits Trends Shaping Today's Workplace
As organizations adapt to the needs of a multigenerational workforce, several emerging trends promise to shape benefits strategy throughout 2025 and beyond. These trends reflect both technological advancement and evolving employee expectations across all age groups.
Flexible Benefits Architecture
The shift toward cafeteria-style benefits reflects employee demand for personalization.
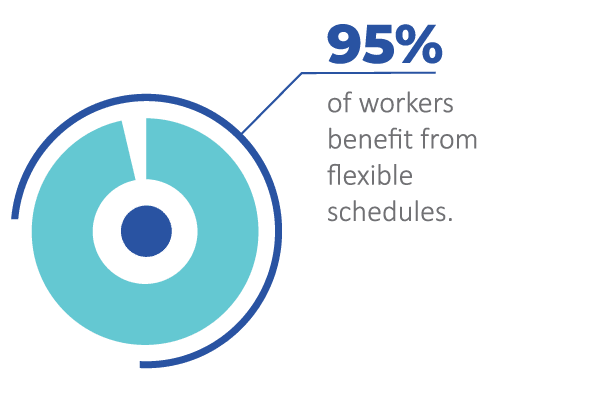
With 95% of workers benefiting from flexible schedules, organizations are applying this flexibility principle to benefits design, enabling employees to tailor packages to their individual needs and life stages.
Lifestyle Spending Accounts
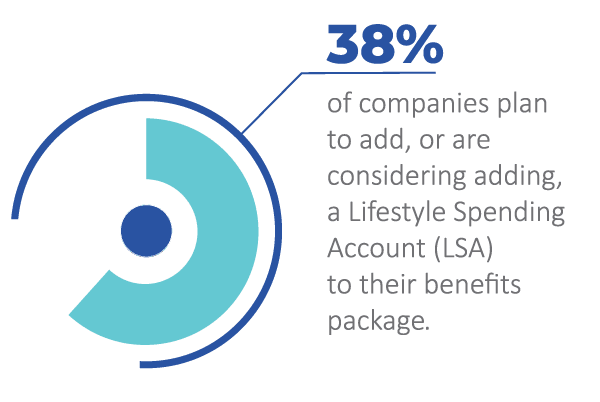
Recent SHRM data shows that 38% of companies plan to add, or are considering adding, a Lifestyle Spending Account (LSA) to their benefits package.
The flexibility of LSAs allows employees to use funds for wellness and lifestyle expenses, tailored to different generational priorities. Whether used for fitness equipment, continuing education, or family care services, LSAs provide personalization without administrative complexity.
Integrated Wellness Ecosystems
Modern wellness programs extend far beyond traditional health benefits, incorporating mental health support, financial wellness, fitness benefits, and holistic wellness approaches.
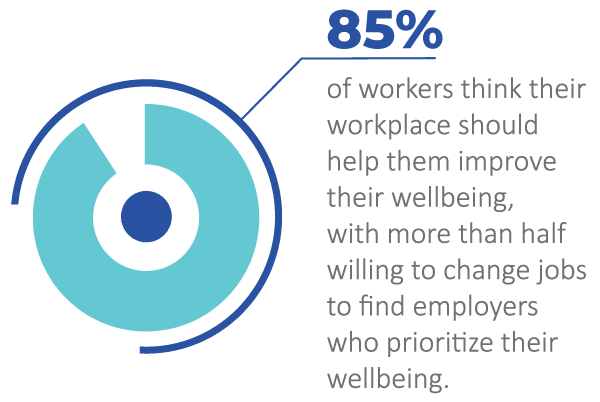
According to Wellhub's Return on Wellbeing 2024, 85% of workers believe employers should help them improve their wellbeing, and over half are willing to change jobs to find employers who does. Personal benefits, such as fitness reimbursements, wellness challenges, subsidized meal services, and cooking classes can be extended via LSAs or in another manner. These programs empower employees to prioritize health in ways that resonate with their values and lifestyles. Currently, 51% of employers with 50+ employees offer some type of wellness program.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Younger generations increasingly evaluate employers based on their demonstrated environmental and social responsibility. Benefits offerings that include sustainable commuting options, volunteer time off, and charitable giving programs not only attract younger talent but also enhance the overall employer brand.
Generational Benefits Preferences
Understanding how each generation prioritizes benefits enables HR leaders and third party administrators to design packages that boost employee engagement while controlling costs.
Generation | Focus | Top Priorities | Emerging Needs |
|---|---|---|---|
Gen Z | Wellness and flexibility |
|
|
Millennials | Purpose and growth |
|
|
Generation X | Practical Support |
|
|
Baby Boomers | Security and stability |
|
|
Strategic Implementation Recommendations
The key to a successful multigenerational benefits strategy is a clear plan that blends data insights with practical execution. These six recommendations provide a framework for organizations seeking to optimize benefits for every generation.
1. Conduct Comprehensive Generational Benefits Assessments
Regular employee surveys across all generations provide the data foundation for informed decisions about benefits. Research shows that employees who feel informed about company benefits are 3x more likely to use them, making education and communication critical components of benefits strategy. Go beyond simple preference questions to understand the "why" behind benefits choices, enabling more strategic decision-making.
2. Design for Flexibility and Choice
Create benefit packages that are easy to manage but still let employees choose what matters most to them. Offer basic universal benefits that meet cross-generational needs, plus optional benefits that appeal to different age groups.
3. Develop Multi-Channel Communication Strategies
Effective benefits communication requires meeting each generation where they are. Combine digital platforms with traditional methods to ensure comprehensive coverage while respecting individual communication preferences.
Strategic Implementation Recommendations
1. Conduct employee surveys
2. Balance flexibility and choice with efficiency
3. Reach employees where they are with multi-channel communications
4. Prioritize universal needs first
5. Anticipate emerging trends
6. Deploy technology, thoughtfully
3. Develop Multi-Channel Communication Strategies
Effective benefits communication requires meeting each generation where they are. Combine digital platforms with traditional methods to ensure comprehensive coverage while respecting individual communication preferences.
4. Build Around Universal Needs
Identify benefits with broad appeal as the foundation of your benefits strategy. Starting with healthcare coverage, financial wellness programs, and flexible work arrangements provides the platform for more targeted generational offerings.
5. Stay Ahead of Emerging Trends
Monitor generational preferences, economic factors, and societal changes to anticipate future needs. Successful benefits programs evolve proactively rather than reactively.
6. Leverage Technology Thoughtfully
Use technology to enhance benefits delivery and personalization while maintaining accessibility for all generations. Ensure digital solutions include human support options and remain user-friendly across all age groups.
Building the Future of Employee Benefits
Third-party administrators offer a winning combination: advanced technology for efficient benefits administration plus trusted advisory relationships that help employers meet diverse generational needs.
Successfully navigating generational differences in employee benefits takes more than understanding what each age group wants. It demands a strategic, data-driven approach that meets universal needs while offering options that appeal to different generations, and stays flexible enough to adapt to future change.
The key insight for benefits professionals is that while generational differences are real, so are individual preferences and life circumstances. The best benefits programs create flexible, comprehensive packages supported by effective communication strategies that treat employees as individuals, not just demographic segments.
With today's tight job market and high employee expectations, understanding and addressing generational preferences is essential. This approach goes beyond legal requirements and beating the competition. It's about creating workplace cultures that value and support every employee, regardless of age or life stage.
Organizations that proactively address generational differences in employee benefits will find themselves better positioned to attract top talent, maintain employee satisfaction, and achieve sustainable business success. By 2034, 80% of the workforce in advanced economies will comprise Millennials, Gen Z, and the first Gen Alphas to become adults. The future belongs to organizations that recognize the strength in generational diversity and harness it through thoughtful, inclusive benefits design.
A multigenerational workforce presents both challenges and opportunities. Companies that embrace this complexity and design benefits programs that serve all employees can turn generational differences from a challenge into a competitive advantage that drives engagement, retention, and business results.
Founded in 1984, DataPath, Inc. is a leading provider of technology, BPO, and contact center solutions for benefits administrators. Contact us today for FREE consultation!

Ready to simplify your benefits administration and grow your business?

